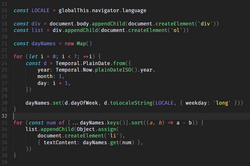
Portal:Computer programming
Portal maintenance status: (September 2019)
|
The Computer Programming Portal
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the application domain, details of programming languages and generic code libraries, specialized algorithms, and formal logic.
Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include analyzing requirements, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), implementation of build systems, and management of derived artifacts, such as programs' machine code. While these are sometimes considered programming, often the term software development is used for this larger overall process – with the terms programming, implementation, and coding reserved for the writing and editing of code per se. Sometimes software development is known as software engineering, especially when it employs formal methods or follows an engineering design process. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1In computing, a loader is the part of an operating system that is responsible for loading programs and libraries. It is one of the essential stages in the process of starting a program, as it places programs into memory and prepares them for execution. Loading a program involves either memory-mapping or copying the contents of the executable file containing the program instructions into memory, and then carrying out other required preparatory tasks to prepare the executable for running. Once loading is complete, the operating system starts the program by passing control to the loaded program code.
All operating systems that support program loading have loaders, apart from highly specialized computer systems that only have a fixed set of specialized programs. Embedded systems typically do not have loaders, and instead, the code executes directly from ROM or similar. In order to load the operating system itself, as part of booting, a specialized boot loader is used. In many operating systems, the loader resides permanently in memory, though some operating systems that support virtual memory may allow the loader to be located in a region of memory that is pageable.
In the case of operating systems that support virtual memory, the loader may not actually copy the contents of executable files into memory, but rather may simply declare to the virtual memory subsystem that there is a mapping between a region of memory allocated to contain the running program's code and the contents of the associated executable file. (See memory-mapped file.) The virtual memory subsystem is then made aware that pages with that region of memory need to be filled on demand if and when program execution actually hits those areas of unfilled memory. This may mean parts of a program's code are not actually copied into memory until they are actually used, and unused code may never be loaded into memory at all. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Large supercomputers such as IBM's Blue Gene/P are designed to heavily exploit parallelism.
Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling. As power consumption (and consequently heat generation) by computers has become a concern in recent years, parallel computing has become the dominant paradigm in computer architecture, mainly in the form of multi-core processors.
In computer science, parallelism and concurrency are two different things: a parallel program uses multiple CPU cores, each core performing a task independently. On the other hand, concurrency enables a program to deal with multiple tasks even on a single CPU core; the core switches between tasks (i.e. threads) without necessarily completing each one. A program can have both, neither or a combination of parallelism and concurrency characteristics.
Parallel computers can be roughly classified according to the level at which the hardware supports parallelism, with multi-core and multi-processor computers having multiple processing elements within a single machine, while clusters, MPPs, and grids use multiple computers to work on the same task. Specialized parallel computer architectures are sometimes used alongside traditional processors, for accelerating specific tasks. (Full article...) -
Image 3

W3sDesign Interpreter Design Pattern UML
In computing, an interpreter is software that executes source code without first compiling it to machine code. An interpreted runtime environment differs from one that processes CPU-native executable code which requires translating source code before executing it. An interpreter may translate the source code to an intermediate format, such as bytecode. A hybrid environment may translate the bytecode to machine code via just-in-time compilation, as in the case of .NET and Java, instead of interpreting the bytecode directly.
Before the widespread adoption of interpreters, the execution of computer programs often relied on compilers, which translate and compile source code into machine code. Early runtime environments for Lisp and BASIC could parse source code directly. Thereafter, runtime environments were developed for languages (such as Perl, Raku, Python, MATLAB, and Ruby), which translated source code into an intermediate format before executing to enhance runtime performance.
Code that runs in an interpreter can be run on any platform that has a compatible interpreter. The same code can be distributed to any such platform, instead of an executable having to be built for each platform. Although each programming language is usually associated with a particular runtime environment, a language can be used in different environments. Interpreters have been constructed for languages traditionally associated with compilation, such as ALGOL, Fortran, COBOL, C and C++. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is dynamically type-checked and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented and functional programming.
Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision and not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Beginning with Python 3.5, capabilities and keywords for typing were added to the language, allowing optional static typing. As of 2026[update], the Python Software Foundation supports Python 3.10, 3.11, 3.12, 3.13, and 3.14, following the project's annual release cycle and five-year support policy. Python 3.15 is currently in the alpha development phase, and the stable release is expected to come out in October 2026."Earlier versions in the 3.x series have reached end-of-life and no longer receive security updates.
Python has gained widespread use in the machine learning community. It is widely taught as an introductory programming language. Since 2003, Python has consistently ranked in the top ten of the most popular programming languages in the TIOBE Programming Community Index, which ranks based on searches in 24 platforms. (Full article...) -
Image 5Forth is a stack-oriented programming language and interactive integrated development environment designed by Charles H. "Chuck" Moore and first used by other programmers in 1970. Although not an acronym, the language's name in its early years was often spelled in all capital letters as FORTH. The FORTH-79 and FORTH-83 implementations, which were not written by Moore, became de facto standards, and an official technical standard of the language was published in 1994 as ANS Forth. A wide range of Forth derivatives existed before and after ANS Forth. The free and open-source software Gforth implementation is actively maintained, as are several commercially supported systems.
Forth typically combines a compiler with an integrated command shell, where the user interacts via subroutines called words.
Words can be defined, tested, redefined, and debugged without recompiling or restarting the whole program. All syntactic elements, including variables, operators, and control flow, are defined as words. A stack is used to pass parameters between words, leading to a Reverse Polish notation style. (Full article...) -
Image 6Ronald Paul "Ron" Fedkiw (born February 27, 1968) is a full professor in the Stanford University department of computer science and a leading researcher in the field of computer graphics, focusing on topics relating to physically based simulation of natural phenomena and machine learning. His techniques have been employed in many motion pictures. He has earned recognition at the 80th Academy Awards and the 87th Academy Awards as well as from the National Academy of Sciences.
His first Academy Award was awarded for developing techniques that enabled many technically sophisticated adaptations including the visual effects in 21st century movies in the Star Wars, Harry Potter, Terminator, and Pirates of the Caribbean franchises. Fedkiw has designed a platform that has been used to create many of the movie world's most advanced special effects since it was first used on the T-X character in Terminator 3: Rise of the Machines. His second Academy Award was awarded for computer graphics techniques for special effects for large scale destruction. Although he has won an Oscar for his work, he does not design the visual effects that use his technique. Instead, he has developed a system that other award-winning technicians and engineers have used to create visual effects for some of the world's most expensive and highest-grossing movies. (Full article...) -
Image 7Jobs introducing the iPhone 4, 2010
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American businessman, inventor, and investor best known for co-founding the technology company Apple Inc. Jobs was also the founder of NeXT and chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar. He was a pioneer of the personal computer revolution of the 1970s and 1980s, along with his early business partner and fellow Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak.
Jobs was born in San Francisco in 1955 and adopted shortly afterwards. He attended Reed College in 1972 before withdrawing that same year. In 1974, he traveled through India, seeking enlightenment before later studying Zen Buddhism. He and Wozniak co-founded Apple in 1976 to further develop and sell Wozniak's Apple I personal computer. Together, the duo gained fame and wealth a year later with production and sale of the Apple II, one of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputers.
Jobs saw the commercial potential of the Xerox Alto in 1979, which was mouse-driven and had a graphical user interface (GUI). This led to the development of the largely unsuccessful Apple Lisa in 1983, followed by the breakthrough Macintosh in 1984, the first mass-produced computer with a GUI. The Macintosh launched the desktop publishing industry in 1985 (for example, the Aldus PageMaker) with the addition of the Apple LaserWriter, the first laser printer to feature vector graphics and PostScript. (Full article...) -
Image 8Mya was an intelligent personal assistant under development by Motorola in the year 2000. Proposed features for the program included the ability to read emails and answer questions 24 hours a day. Mya was intended to work with an internet service Motorola was developing called Myosphere, and was planned to be a paid service that would eventually be used by other mobile carriers. A female computer-generated character was created to represent Mya in advertising. While the quality of the character's animation was praised, it received criticism for being over sexualised.
Both the character and the program were announced to the public via an advertisement in March 2000, though the program was not ready for use at that time. Despite the announcement generating a considerable amount of attention, little was heard regarding the project in subsequent months. The program was never officially released nor cancelled, though the trademarks for both Myosphere and Mya were abandoned by Motorola in 2002. The name Mya was believed to be a play on the words 'My assistant'. (Full article...) -
Image 9Object Pascal is an extension to the programming language Pascal that provides object-oriented programming (OOP) features such as classes and methods.
The language was originally developed by Apple Computer as Clascal for the Lisa Workshop development system. As Lisa gave way to Macintosh, Apple collaborated with Niklaus Wirth, the author of Pascal, to develop an officially standardized version of Clascal. This was renamed Object Pascal. Through the mid-1980s, Object Pascal was the main programming language for early versions of the MacApp application framework. The language lost its place as the main development language on the Mac in 1991 with the release of the C++-based MacApp 3.0. Official support ended in 1996.
Symantec also developed a compiler for Object Pascal for their Think Pascal product, which could compile programs much faster than Apple's own Macintosh Programmer's Workshop (MPW). Symantec then developed the Think Class Library (TCL), based on MacApp concepts, which could be called from both Object Pascal and THINK C. The Think suite largely displaced MPW as the main development platform on the Mac in the late 1980s. (Full article...) -
Image 10

The source code for a computer program in C. The gray lines are comments that explain the program to humans. When compiled and run, it will give the output "Hello, world!".
A programming language is an engineered language for expressing computer programs.
Programming languages typically allow software to be written in a human readable manner.
Execution of a program requires an implementation. There are two main approaches for implementing a programming language – compilation, where programs are compiled ahead-of-time to machine code, and interpretation, where programs are directly executed. In addition to these two extremes, some implementations use hybrid approaches such as just-in-time compilation and bytecode interpreters. (Full article...) -
Image 11Logotype used on the cover of the first edition of The C Programming Language
C is a general-purpose programming language created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie. By design, C gives the programmer relatively direct access to the features of the typical CPU architecture, customized for the target instruction set. It has been and continues to be used to implement operating systems (especially kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is used on computers that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems.
A successor to the programming language B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming languages, with C compilers available for practically all modern computer architectures and operating systems. The book The C Programming Language, co-authored by the original language designer, served for many years as the de facto standard for the language. C has been standardized since 1989 by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and, subsequently, jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
C is an imperative procedural language, supporting structured programming, lexical variable scope, and recursion, with a static type system. It was designed to be compiled to provide low-level access to memory and language constructs that map efficiently to machine instructions, all with minimal runtime support. Despite its low-level capabilities, the language was designed to encourage cross-platform programming. A standards-compliant C program written with portability in mind can be compiled for a wide variety of computer platforms and operating systems with few changes to its source code. (Full article...) -
Image 12
JavaScript (JS) is a programming language and core technology of the Web, alongside HTML and CSS. It was created by Brendan Eich in 1995. As of 2025, the overwhelming majority of websites (98.9%) uses JavaScript for client side webpage behavior.
Web browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine that executes the client code. These engines are also utilized in some servers and a variety of apps. The most popular runtime system for non-browser usage is Node.js.
JavaScript is a high-level, often just-in-time–compiled language that conforms to the ECMAScript standard. It has dynamic typing, prototype-based object-orientation, and first-class functions. It is multi-paradigm, supporting event-driven, functional, and imperative programming styles. It has application programming interfaces (APIs) for working with text, dates, regular expressions, standard data structures, and the Document Object Model (DOM). (Full article...) -
Image 13Rust is a general-purpose programming language. It is noted for its emphasis on performance, type safety, concurrency, and memory safety.
Rust supports multiple programming paradigms. It was influenced by ideas from functional programming, including immutability, higher-order functions, algebraic data types, and pattern matching. It also supports object-oriented programming via structs, enums, traits, and methods. Rust is noted for enforcing memory safety (i.e., that all references point to valid memory) without a conventional garbage collector; instead, memory safety errors and data races are prevented by the "borrow checker", which tracks the object lifetime of references at compile time.
Software developer Graydon Hoare created Rust in 2006 while working at Mozilla, which officially sponsored the project in 2009. The first stable release, Rust 1.0, was published in May 2015. Following a layoff of Mozilla employees in August 2020, four other companies joined Mozilla in sponsoring Rust through the creation of the Rust Foundation in February 2021. (Full article...) -
Image 14
William Henry Gates III (born October 28, 1955) is an American businessman and philanthropist. A pioneer of the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s and 1980s, he co-founded the software company Microsoft in 1975 with his childhood friend Paul Allen. Gates became the world's then-youngest billionaire in 1987, at age 31. This followed Microsoft's initial public offering in the previous year and subsequent stock increase. Forbes magazine ranked him as the world's wealthiest person for 18 out of 24 years between 1995 and 2017, including 13 years consecutively from 1995 to 2007. Gates became the first centibillionaire in 1999, when his net worth briefly surpassed US$100 billion. According to Forbes, as of May 2025, his net worth stood at US$115.1 billion, making him the thirteenth-richest individual in the world.
Born and raised in Seattle, Washington, Gates was privately educated at Lakeside School, where he befriended Allen and developed his computing interests. In 1973, he enrolled at Harvard University, where he took classes including Math 55 and graduate- level computer science courses, but he dropped out in 1975 to co-found and lead Microsoft. He served as its CEO for the next 25 years and also became president and chairman of the board when the company was incorporated in 1981. Succeeded as CEO by Steve Ballmer in 2000, he transitioned to chief software architect, a position he held until 2008. He stepped down as chairman of the board in 2014 and became technology adviser to CEO Satya Nadella and other Microsoft leaders, a position he still holds. He resigned from the board in 2020.
Over time, Gates reduced his role at Microsoft to focus on his philanthropic work with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the world's largest private charitable organization, which he and his then-wife, Melinda French Gates, co-chaired from 2000 until 2024. Focusing on areas including health, education, and poverty alleviation, Gates became known for his efforts to combat transmissible diseases such as tuberculosis, malaria, and polio. After French Gates resigned as co-chair following the couple's divorce, the foundation was renamed the Gates Foundation, with Gates as its sole chair. (Full article...) -
Image 15SNOBOL (StriNg Oriented and symBOlic Language) is a series of programming languages developed between 1962 and 1967 at AT&T Bell Laboratories by David J. Farber, Ralph Griswold and Ivan P. Polonsky, culminating in SNOBOL4. It was one of a number of text-string-oriented languages developed during the 1950s and 1960s; others included COMIT and TRAC. Despite the similar name, it is entirely unlike COBOL.
SNOBOL4 stands apart from most programming languages of its era by having patterns as a first-class data type, a data type whose values can be manipulated in all ways permitted to any other data type in the programming language, and by providing operators for pattern concatenation and alternation. SNOBOL4 patterns are a type of object and admit various manipulations, much like later object-oriented languages such as JavaScript whose patterns are known as regular expressions. In addition SNOBOL4 strings generated during execution can be treated as programs and either interpreted or compiled and executed (as in the eval function of other languages).
SNOBOL4 was quite widely taught in larger U.S. universities in the late 1960s and early 1970s and was widely used in the 1970s and 1980s as a text manipulation language in the humanities. (Full article...)
Selected images
-
Image 3Margaret Hamilton standing next to the navigation software that she and her MIT team produced for the Apollo Project.
-
Image 4Partial view of the Mandelbrot set. Step 1 of a zoom sequence: Gap between the "head" and the "body" also called the "seahorse valley".
-
Image 5This image (when viewed in full size, 1000 pixels wide) contains 1 million pixels, each of a different color.
-
Image 6A head crash on a modern hard disk drive
-
Image 7Deep Blue was a chess-playing expert system run on a unique purpose-built IBM supercomputer. It was the first computer to win a game, and the first to win a match, against a reigning world champion under regular time controls. Photo taken at the Computer History Museum.
-
Image 8Stephen Wolfram is a British-American computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer science, mathematics, and in theoretical physics.
-
Image 9Output from a (linearised) shallow water equation model of water in a bathtub. The water experiences 5 splashes which generate surface gravity waves that propagate away from the splash locations and reflect off of the bathtub walls.
-
Image 10GNOME Shell, GNOME Clocks, Evince, gThumb and GNOME Files at version 3.30, in a dark theme
-
Image 11Partial map of the Internet based on the January 15, 2005 data found on opte.org. Each line is drawn between two nodes, representing two IP addresses. The length of the lines are indicative of the delay between those two nodes. This graph represents less than 30% of the Class C networks reachable by the data collection program in early 2005.
-
Image 12Ada Lovelace was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognize that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
-
Image 14A view of the GNU nano Text editor version 6.0
-
Image 15A lone house. An image made using Blender 3D.
-
Image 16Grace Hopper at the UNIVAC keyboard, c. 1960. Grace Brewster Murray: American mathematician and rear admiral in the U.S. Navy who was a pioneer in developing computer technology, helping to devise UNIVAC I. the first commercial electronic computer, and naval applications for COBOL (common-business-oriented language).
-
Image 18An IBM Port-A-Punch punched card
Did you know? - load more entries

- ... that the Gale–Shapley algorithm was used to assign medical students to residencies long before its publication by Gale and Shapley?
- ... that the study of selection algorithms has been traced to an 1883 work of Lewis Carroll on how to award second place in single-elimination tournaments?
- ... that Phil Fletcher as Hacker T. Dog caused Lauren Layfield to make the "most famous snort" in the United Kingdom in 2016?
- ... that the 2024 psychological horror game Mouthwashing utilises non-diegetic scene transitions that mimic glitches and crashes?
- ... that both Thackeray and Longfellow bought paintings by Fanny Steers?
- ... that NATO was once targeted by a group of "gay furry hackers"?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
- There are many users interested in computer programming, join them.
Computer programming news
No recent news
Topics
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus