门面模式
外观

门面模式(英語:facade pattern),也翻译为外观模式,是軟件工程中常用的一種軟件設計模式[1],它為子系統中的一組介面提供一個統一的高層介面,使得子系統更容易使用。
概述
[编辑]门面模式是面向对象程序设计中常用的一个设计模式。门面的概念类似于一个建筑学中的立面,门面作为一个前端接口来屏蔽更复杂的底层或结构代码。门面模式可以用来[2]:
- 通用简化的API屏蔽与更复杂的内部组件和结构, 以提高软件库的可读性和可用性。
- 为更通用的功能提供上下文特定的接口。
- 在广泛更新重构单层系统或紧密耦合的軟件系统, 提供一个简化的启动点,更有利于更多的松耦合代码。
当一个系统非常复杂或难以理解时,开发人员通常会使用门面设计模式,因为该系统有许多相互依赖的类,或者因为其源代码不可用。门面模式隐藏了更大系统的复杂性,为客户端提供了一个更简单的接口。通常会涉及到一个wrapper包含客户端所需的一组成员的。这些成员代表门面的客户端访问系统并隐藏实现细节。
結構
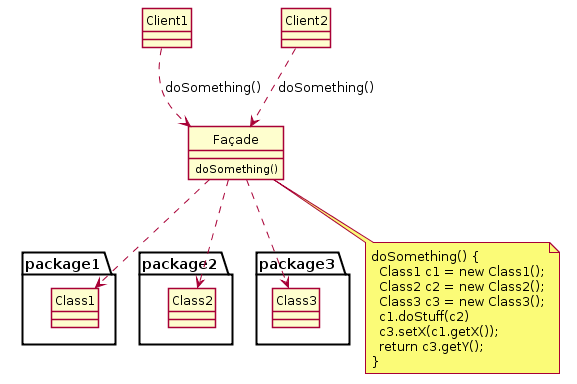
[编辑]- Facade
- 這個門面類為子系統中Packages 1、2、3提供一個共同的對外介面(接口)
- Clients
- 客戶對象通過一個門面介面讀寫子系統中各介面的數據資源。
- Packages
- 客戶可以通過門面介面讀取的内部庫。
示例
[编辑]C++
[编辑]class CPU {
public:
void freeze() { ... }
void jump(long position) { ... }
void execute() { ... }
}
class Memory {
public:
void load(long position, char* data) {
...
}
}
class HardDrive {
public:
char* read(long lba, int size) {
...
}
}
/* Façade */
class Computer {
public:
void startComputer() {
cpu.freeze();
memory.load(BOOT_ADDRESS, hardDrive.read(BOOT_SECTOR, SECTOR_SIZE));
cpu.jump(BOOT_ADDRESS);
cpu.execute();
}
}
/* Client */
class You {
public:
void start(String[] args) {
Computer facade = new Computer();
facade.startComputer();
}
}
Java
[编辑]這是一個抽象的範例。一個客戶“you”通過門面介面“computer”獲取計算機内部複雜的系統信息。
/* Complex parts */
class CPU {
public void freeze() { ... }
public void jump(long position) { ... }
public void execute() { ... }
}
class Memory {
public void load(long position, byte[] data) {
...
}
}
class HardDrive {
public byte[] read(long lba, int size) {
...
}
}
/* Façade */
class Computer {
public void startComputer() {
cpu.freeze();
memory.load(BOOT_ADDRESS, hardDrive.read(BOOT_SECTOR, SECTOR_SIZE));
cpu.jump(BOOT_ADDRESS);
cpu.execute();
}
}
/* Client */
class You {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer facade = new Computer();
facade.startComputer();
}
}
C#
[编辑]// Facade pattern -- Structural example
using System;
namespace DoFactory.GangOfFour.Facade.Structural {
// Mainapp test application
class MainApp {
public static void Main() {
Facade facade = new Facade();
facade.MethodA();
facade.MethodB();
// Wait for user
Console.Read();
}
}
// "Subsystem ClassA"
class SubSystemOne {
public void MethodOne() {
Console.WriteLine(" SubSystemOne Method");
}
}
// Subsystem ClassB"
class SubSystemTwo {
public void MethodTwo() {
Console.WriteLine(" SubSystemTwo Method");
}
}
// Subsystem ClassC"
class SubSystemThree {
public void MethodThree() {
Console.WriteLine(" SubSystemThree Method");
}
}
// "Facade"
class Facade {
SubSystemOne one;
SubSystemTwo two;
SubSystemThree three;
public Facade() {
one = new SubSystemOne();
two = new SubSystemTwo();
three = new SubSystemThree();
}
public void MethodA() {
Console.WriteLine("\nMethodA() ---- ");
one.MethodOne();
two.MethodTwo();
}
public void MethodB() {
Console.WriteLine("\nMethodB() ---- ");
two.MethodTwo();
three.MethodThree();
}
}
}
Python
[编辑]下面是Python的例子,这里的类可以放置在不同的模块或包之中:
class CPU():
def freeze(self): pass
def jump(self, position): pass
def execute(self): pass
class Memory():
def load(self, position, data): pass
class HardDrive():
def read(self, lba, size): pass
class Computer():
def __init__(self, *, cpu, mem, hd):
self.cpu = cpu
self.mem = memory
self.hd = hard_drive
def start_computer(self):
self.cpu.freeze();
self.mem.load('BOOT_ADDRESS',
self.hd.read('BOOT_SECTOR', 'SECTOR_SIZE'))
self.cpu.jump('BOOT_ADDRESS');
self.cpu.execute();
facade = Computer(cpu=CPU(), mem=Memory(), hd=HardDrive())
facade.start_computer()
引用
[编辑]- ^ Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson, John Vlissides. Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software
 . Addison Wesley. 1994: 185ff. ISBN 0-201-63361-2.
. Addison Wesley. 1994: 185ff. ISBN 0-201-63361-2.
- ^ The Facade design pattern - Problem, Solution, and Applicability. w3sDesign.com. [2017-08-12]. (原始内容存档于2020-06-12).