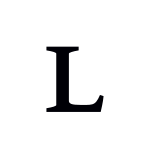Voiced velar lateral approximant
| Voiced velar lateral approximant | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ʟ | |||
| IPA number | 158 | ||
| Audio sample | |||
| Encoding | |||
| Entity (decimal) | ʟ | ||
| Unicode (hex) | U+029F | ||
| X-SAMPA | L\ | ||
| Braille | |||
| |||
| Voiced velar lateral tap | |
|---|---|
| ʟ̆ | |
| Audio sample | |
| Encoding | |
| X-SAMPA | L\_X |
| Voiced uvular lateral approximant | |
|---|---|
| ʟ̠ | |
| IPA number | 158 414 |
| Audio sample | |
| Encoding | |
| X-SAMPA | L\_- |
A voiced velar lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound, used as a distinct consonant in a very small number[1] of spoken languages in the world. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that has represented this sound since 1989 is ⟨ʟ⟩, a small capital letter l.
Velar laterals often involve a prestopped realization [ᶢʟ].[2]
According to Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996), the extremely short duration of /ʟ/ in intervocalic position (20–30 ms) in some of the languages in New Guinea, such as Kanite and Melpa, warrants calling it a voiced velar lateral tap. The IPA has no specific symbol for this sound, but it may be represented with a breve for extra-short, such as ⟨ʟ̆⟩, to indicate a tapped consonant.
It is reported that some dialects of English may have a voiced uvular lateral approximant,[3] which can be represented in the IPA as ⟨ʟ̠⟩ (a retracted ⟨ʟ⟩), though evidence of this consonant is limited.
Features
[edit]Features of a voiced velar lateral approximant:
- Its manner of articulation is approximant, which means it is produced by narrowing the vocal tract at the place of articulation, but not enough to produce a turbulent airstream.
- Its place of articulation is velar, which means it is articulated with the back of the tongue (the dorsum) at the soft palate.
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is an oral consonant, which means that air is not allowed to escape through the nose.
- It is a lateral consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream over the sides of the tongue, rather than down the middle.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air only with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
A velar lateral [ʟ] involves no contact of the tip of the tongue with the roof of the mouth: just like for a velar stop [ɡ], the only contact takes place between the back of the tongue and the velum. This contrasts with a velarized alveolar lateral approximant [ɫ] – also known as the dark l in English feel [fiːɫ] – for which the apex touches the alveolar ridge.[4]
Occurrence
[edit]Velar
[edit]| Language | Word | IPA | Meaning | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Southern US[5] | middle | [ˈmɪɾʟ̩] | 'middle' | May occur before or after a velar consonant, as in milk and cycle, when assimilating /ʊ/, as in wolf, or before labial consonants, as in help. See English phonology |
| full | [ˈfʟ̩ː] | 'full' | |||
| Franco-Provençal[6] | grêlon | [ˈɡriʟœ] | 'hailstone' | Valais dialects | |
| Hiw[7] | r̄evr̄ov | [ɡ͡ʟəβˈɡ͡ʟɔβ] | 'evening' | May be realized as prestopped [ᶢʟ], affricate [ɡʟ̝], or laterally released stop [ɡᶫ]. | |
| Melpa[8] | paⱡa | ⓘ | 'fence' | May be realized as prestopped [ᶢʟ] or tapped [ʟ̆]. | |
| Mid-Wahgi[9] | aglagle | [aʟaʟe] | 'dizzy' | May be realized as prestopped [ᶢʟ]. | |
Uvular
[edit]| Language | Word | IPA | Meaning | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Some American speakers[3] | wool | [wʊʟ̠] | 'wool' | May be velar or simply alveolar instead. See English phonology. |
See also
[edit]- Voiceless velar lateral approximant, [ʟ̥]
- Velarized alveolar lateral approximant, [ɫ]
- Voiceless alveolar lateral fricative, [ɬ]
- Voiced velar lateral fricative, [ʟ̝]
- Voiceless velar lateral fricative, [ʟ̝̊] or extIPA [𝼄]
- Index of phonetics articles
Notes
[edit]- ^ François (2010), pp. 422–426.
- ^ François (2010), p. 425.
- ^ a b Cruttenden (2014), p. 221.
- ^ François (2010), p. 423.
- ^ Wells (1982), p. 551.
- ^ [1]
- ^ François (2010), p. 419.
- ^ Ladefoged (2005), p. 169.
- ^ Roca & Johnson (1999), p. 73.
References
[edit]- Cruttenden, Alan (2014), Gimson's Pronunciation of English (8th ed.), Routledge, ISBN 9781444183092
- François, Alexandre (2010), "Phonotactics and the prestopped velar lateral of Hiw: resolving the ambiguity of a complex segment" (PDF), Phonology, 27 (3): 393–434, doi:10.1017/s0952675710000205, S2CID 62628417
- Ladefoged, Peter; Maddieson, Ian (1996). The Sounds of the World's Languages. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-19815-6.
- Ladefoged, Peter (2005), Vowels and Consonants (2nd ed.), Blackwell
- Roca, Iggy; Johnson, Wyn (1999), A Course in Phonology, Blackwell Publishing
- Wells, John C. (1982). Accents of English. Vol. 3: Beyond the British Isles (pp. i–xx, 467–674). Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511611766. ISBN 0-52128541-0.